Greece is experiencing an early surge of seasonal flu, mirroring trends across the Northern Hemisphere. Health officials have confirmed the presence of the K subvariant of the influenza A(H3N2) virus, which has been circulating worldwide.
According to a risk assessment released by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) on November 20, 2025, the K subvariant is considered a moderate risk for the general population. However, it poses a high risk for vulnerable groups, including adults over 65, pregnant women, people with chronic illnesses, immunocompromised individuals, and residents of long-term care facilities.
In anticipation of the upcoming holiday season, Greece’s National Public Health Organization (EODY) has issued several key recommendations:
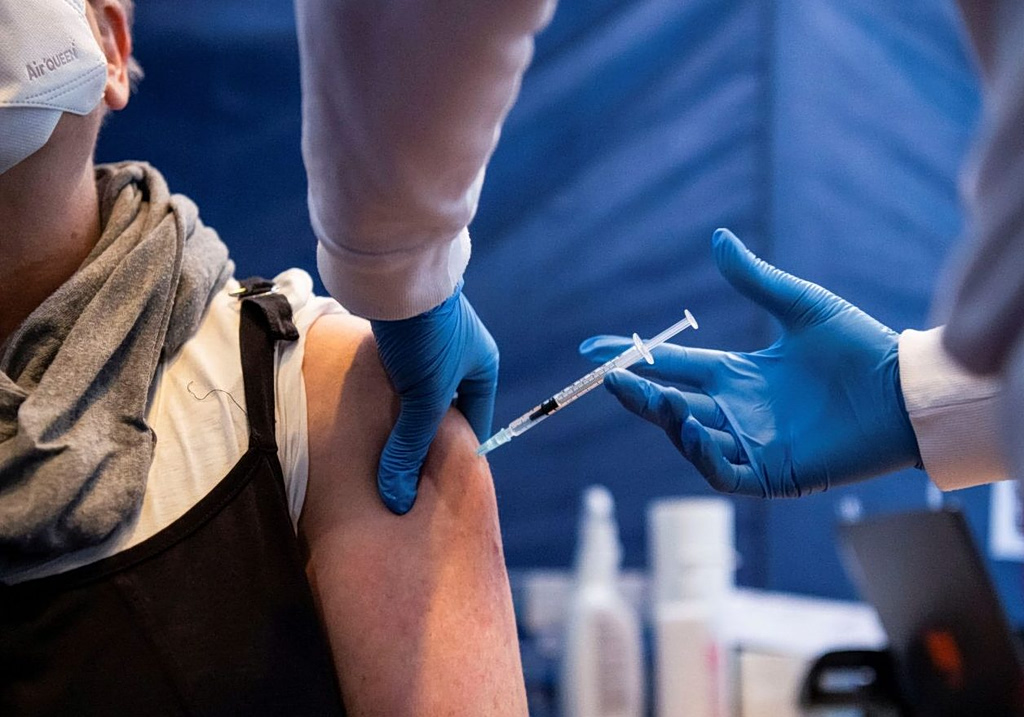
- Immediate flu vaccination, particularly for high-risk groups, remains the most effective preventive measure against severe illness and death.
- Prompt antiviral treatment should be initiated for high-risk individuals showing flu-like symptoms, even without a positive test. In cases of outbreak in closed facilities, prophylactic antiviral therapy should be considered.
- Protective measures such as frequent handwashing, avoiding touching the face, wearing masks in crowded indoor spaces for at-risk individuals, maintaining respiratory hygiene, ensuring proper ventilation, and staying home if symptomatic are strongly advised.